剑指offer
按牛客网的顺序。
二维数组中的查找
在一个二维数组中(每个一维数组的长度相同),每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
1 | class Solution { |
按牛客网的顺序。
在一个二维数组中(每个一维数组的长度相同),每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
1 | class Solution { |
内部监听的事件以
epitem组织为一个红黑树注册和事件添加到epoll的rdlist都是通过调用f_op->poll
注册时是通过将epoll添加到文件的wait_queue_head中
rdlist上的epitem通常是由被监听文件自己挂上去的
fs/eventpoll.cepoll_create (SYSCALL_DEFINE1(epoll_create) -> do_epoll_create1 | // 有 strc |
1 | struct wait_queue_head { |
现代计算机使用UEFI,可以一次加载超过512B的boot sector。
以下为JOS启动流程。
960KB~1MB地址出。MBR)到0x7c00处。如果这个扇区最后两个字节是0x55和0XAA表明可以启动,否则不能。boot.S,其中的主要流程包括:A20线(兼容性问题,寻找范围更大),加载段表(lgdt gdtdesc)(包含操作系统内核的段信息),寻址方式变为segment:offsetCR0寄存器的CR0_PE_ON为1:从实模式(16bit寻址)切换到保护模式(32bit寻址)实模式下寻址方式:物理地址 = 段基址<<4 + 段内偏移,早期寄存器是16位,地址线是20位,只能访问1MB%cs = xff00,%ax = 0x0110,则物理地址为:0xff00<<4 + 0x0110 = 0xff110segment:offset,segment找到该段的基址base,(检查flags可访问的话)之后直接与offset相加得到线性地址,如果没有分页则线性地址等于物理地址。segment:offset0x7c00call bootmain:即boot/main.c中的代码bootmain的主要工作:kernel加载到内存里的0x10000处,其中.text段在0x100000处。并执行ELFHDR->e_entry(0x10000C处,boot/entry.S)。内核映像为ELF格式。0xf0110000),之后call i386_init起源:最早出现于 19 世纪 70 年代,被用于处理 memory-mapeed I/O (MMIO)带来的问题。
1 | unsigned int *p = GetMagicAddress(); // 可能不是内存地址而是I/O设备地址 |
作用:
1 | a = f(c); |
-O2也不会gcc的优化仅保证一段程序的输出,在优化前后无变化。可能会改变前后两行变量的赋值顺序。volatile变量与非volatile变量间的赋值顺序也可能被调换,JAVA不会。volatile变量间的赋值顺序不会被调换volatile仅保证编译器不会乱序,不保证CPU乱序使用场景:
libpg_query:裁剪出的postgresql的语法解析和词法解析。
BuildParseTree:对parser生成的语法树进行解析,得到SelectStatement,其中记录了语句的各个组件。
1 | class SelectStatement : public SQLStatement { |

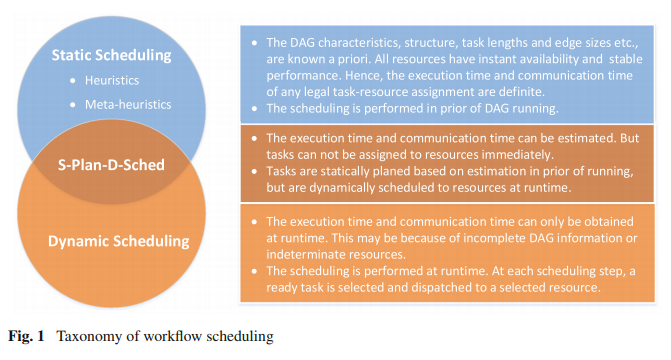
- Task selection Select the first task from the scheduling list;
- Resource selection Allocate the task to selected resource.
static: priorities are constructed before any task allocation
dynamic: the priorities of unscheduled tasks are recomputed after each task scheduling step