Workflow scheduling in cloud: a survey
Modeling and definition

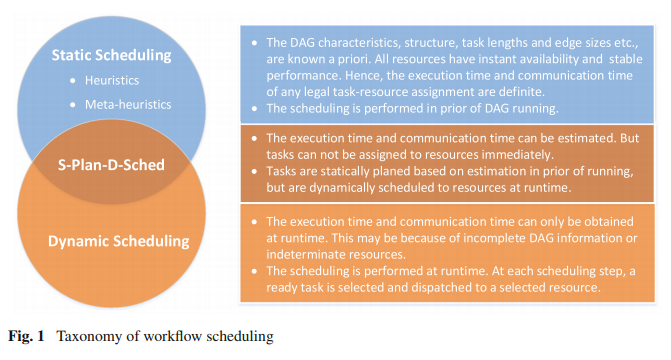
static workflow scheduling
- Task selection Select the first task from the scheduling list;
- Resource selection Allocate the task to selected resource.
List scheduling heuristic
static: priorities are constructed before any task allocation
dynamic: the priorities of unscheduled tasks are recomputed after each task scheduling step
List Scheduling Algorithm
Critical-Path algorithm
Parallel sequencing and assembly line problems (1961)
自底向上,每次选择已经准备好的节点分配到准备好的机器上, 离 $exit$ 节点路径长的优先调度
忽略消息传输时间
Modified Critical-Path (MCP) algorithm
Hypertool A Programming Aid for Message-Passing Systems (1990)
MCP Revisited (2000)
每次选择 $ALAP$ 时间最小的节点进行调度, 当有多台机器可用时, 选择调度后整体通信开销最小的

Dynamic-Level Scheduling (DLS) algorithm
A Compile-Time Scheduling Heuristic for Interconnection-Constrained Heterogeneous Processor Architectures (1993)
Highest Levels First with Estimated Times (HLEFT) algorithm : Just like Critical-Path algorithm
Highest Dynamic Levels First with Estimated Times (HDLEFT) algorithm
先选就绪P, 再选合适的task, 或者两个同时考虑一起选的方式较优
HDLEFT’s inherent flaw: 限制了一个可执行的任务只能从当前就绪的处理器中选择一个执行. 因为有 global clock 的存在
Dynamic Level Scheduling (DLS) algorithm
Static Level: 当前节点到 exit 节点的所有执行时间之和, 不包括通信时间
Dynamic Level: $DL(N_i, P_j, \sum) = SL(N_i) - \max [DA(N_i, P_j, \sum), TF(P_j, \sum)]$